The regenerative medicine, a potential treatment for various diseases and injuries, is becoming more recognized as a promising field. Many professional athletes have begun to take advantage of this growing trend to prolong their careers by finding treatments to help them heal faster after an injury.
Stem cell therapy has become one option that athletes consider taking advantage of today. Regenerative medicine services such as Walker Spine & Sport and others are now offering stem cell therapies as a potential treatment for various issues they may face.
If you’re an athlete considering stem cell therapy, here are ten things you should know:
Contents
1. What Are Stem Cells?
These undifferentiated cells renew themselves and become specialized cells like muscles, blood vessels, nerves, and bones. Stem cells take the role of a repair system for the body by replacing damaged tissue with new healthy tissue.
2. What Are The Facts About Stem Cells?
Here are the facts that athletes need to know about stem cells:
-
Stem Cell Accelerates Injury Recovery
Theoretically, stem cell treatments are designed to aid with injury recovery. Stem cells can divide and create new cells that can replace damaged or dead cells, which helps speed up the process of healing and recovery from injuries.
Your body regenerates itself naturally at a slow rate with age. Stem cells can be used to speed up the natural tissue repair process for those who don’t have enough stem cells in their bodies to promote faster healing on their own.
-
Stem Cells Are Present In Your Body
Your body naturally contains stem cells programmed to create new, healthy tissues when you’re injured. However, training can reduce the number of available stem cells in your body and prolong recovery.
If you’re looking to take advantage of stem cell treatments as a way to help with injury healing, you’re not alone. Many professional athletes have begun utilizing this form of treatment to prolong their careers and battle the effects of aging.
-
Stem Cells Can Be Collected And Transplanted
If you’re injured, stem cells can be collected from your blood or bone marrow and then transplanted back into your body to help encourage tissue regeneration. The transplanted stem cells will help create new healthy tissue to replace the damaged tissue.
-
Physical Activity Affects Your Body’s Stem Cell Count
It’s necessary to let your body rest and recover after strenuous physical activity. If you’re constantly putting stress on your body, it’ll begin to use up stem cells faster than they can be created naturally within the body. Over time, this causes a decrease in the number of available stem cells, leading to a longer recovery time for injuries.
3. How Are Stem Cells Used For Treatment?
There are a few ways that stem cells can be used for treatment:
- As therapy directly into the site of injury or damage
- Injection into the bloodstream to circulate throughout the body
- Harvesting and storage of stem cells from the patient’s blood or bone marrow
- Use of stem cells from a donor source
4. What Is A Stem Cell Treatment?
Stem cell treatments can be referred to as regenerative medicine—a branch of medicine that believes in the body’s ability to repair itself and works toward speeding up this process. The stem cells come from embryonic, fetal, and adult (the most widely used type). All three can develop into many different cells that make up the body.
As technology improves continuously, scientists can take stem cells from any part of the body and then multiply them in a lab before reinjecting them into the patient. It speeds up their process for being developed into usable cells to help repair parts of the body that have been damaged.
Athletes have begun using stem cell treatments for various reasons—to help heal injuries, battle age-related muscle degeneration, and even be a potential preventative measure against sports-related injuries.
Since stem cell treatments are relatively new, so there’s still a lot of unknown information about how they work and their long-term effects.
5. What Are Its Procedures?
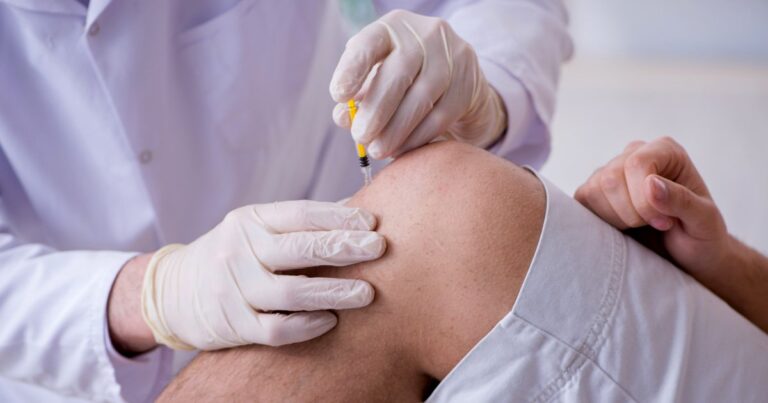
Stem cell treatment has two main types: injection and surgical implantation.
- Injection: In the injection method, cells are extracted from a patient’s body fat and then injected into an injured area of their body with a needle. The procedure is minimally invasive, allowing athletes to recover quickly.
- Surgical Implantation: Alternatively, stem cells can be harvested from an outside donor. One advantage is that the cells are always available since there’s no risk of rejection, but a disadvantage is that it takes much longer for the injured area to heal (up to 18 months) fully.
The first step in stem cell treatment is determining if the patient is a good candidate. It can be done through various medical tests, including blood tests and scans. It’s important to note that stem cell treatments are different from organ transplants.
If you meet with your doctor and determine that you’d be a good candidate for treatment, the next step is to discuss what kind of injury you’re dealing with, how severe it is, and where exactly the damage has in your body occurred.
During this time, your doctor will likely ask you to ease up on the physical activity from which you got your injury in the first place, if possible, and start healing naturally. It’s because more strenuous physical activity could hinder how well your body will respond to stem cell treatment.
If treatment is deemed appropriate by both you and your doctor, then it’s time to harvest stem cells from your body. Often, this is done from a person’s fat deposits using a standard liposuction procedure.
Once the stem cells have been harvested, they’re mixed with a solution and centrifuged to separate them from other cell types. They’ll then be ‘seeded’ onto a special tissue culture to grow and multiply. The cells will be monitored every two to three days, ensuring that their development progresses well.
Once the cells have reached a sufficient quantity, usually within one or two months, they’re ready to be injected into your body in the location of your injury. This process is minimally invasive and causes very little discomfort for the patient.
After your injection, it’ll take approximately one to three months for the stem cells to develop into a new muscle or other tissue in your body (depending on where they were injected). It’s the period when you should start noticing a reduction in pain and an improvement in function.
According to recent research, stem cell treatments can treat injuries in athletes, but it’s important to note that they’re not an immediate fix; there’s no instant relief after the injection.
6. What Are The Benefits Of Stem Cell Treatments?

There are a few potential benefits of stem cell treatments:
- Healing Injuries Faster: One of the main benefits athletes hope to gain from stem cell treatments is its ability to help heal injuries faster. Some evidence suggests stem cells can help the body regenerate tissue and promote healing.
- Reducing Inflammation: Stem cells have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help to reduce swelling and pain.
- Preventing Injuries: Another potential benefit of stem cells is they could be used as a preventative measure against sports-related injuries. Scientists are still exploring this possibility, but some evidence suggests stem cells may help protect the body from damage.
7. What Are The Risks Of Stem Cell Treatments?
There are also risks associated with stem cell treatments, as with any other medical procedures. Some of the potential risks include:
- Rejection: One of the biggest risks is that the body will reject the stem cells, which can cause serious health complications.
- Side Effects: Another risk is that the stem cells may cause side effects in the treated area such as pain or infection.
- Overtreatment: Finally, there’s a risk of overtreating an injury with stem cells, damaging the surrounding healthy tissue.
8. What Are The Other Potential Benefits?

Although stem cell treatments are typically associated with sports injuries, there are other potential benefits to this treatment such as:
- Treating Arthritis: Stem cells have been used in some clinical trials to see if they can help people suffering from arthritis. Often, arthritis is treated using corticosteroids, which can have several side effects. Instead, some people are turning to stem cell treatments as a possible alternative.
- Other Diseases: Stem cells have also been used to treat diseases that affect the brain and spinal cord such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
9. How Much Does A Stem Cell Treatment Cost?
The price of a stem cell treatment varies depending on the type of injury and the number of cells injected. For example, a typical treatment to regenerate a tendon would include five million cells at the cost of USD$5,000 per million cells. Treating an Achilles injury could cost up to USD$25,000 due to the larger quantity of stem cells needed for this type of injury.
10. How Do You Find A Qualified Doctor?
If you’re considering stem cell treatment for an athletic injury, it’s essential to do your research and find a qualified doctor to provide the treatment.
Since not all doctors are well-versed in stem cell treatments, you must choose one who has experience performing these types of procedures before you commit to anything. Ask for recommendations from friends or family members, read online reviews, and ask other athletes about their experiences with a given provider.
You can also check if your insurance will cover the cost of stem cell treatments before committing to anything, so you know what to expect from a financial standpoint.
Final Note
Though stem cell treatments don’t necessarily equate to a miracle cure, they’ve been shown to provide some relief and healing for athletes with various injuries. If you’re considering this type of treatment, do your research and find a qualified doctor to help you get back in the game.

















